©2021 Reporters Post24. All Rights Reserved.
Today, automatic transmission bikes from the likes of Yamaha and Honda mainly constitute either DCTs or AMTs. But CFMoto is exploring outside the box with its upcoming motorcycle. It has a scooter-like transmission, which is primarily infamous for its rubberband effect and restrictions on exploiting the engine’s full potential. The Chinese motorcycle maker is willing to bet the odds on a parallel-twin motorcycle with a CVT gearbox.
CFMoto Has Patented A CVT Motorcycle Engine
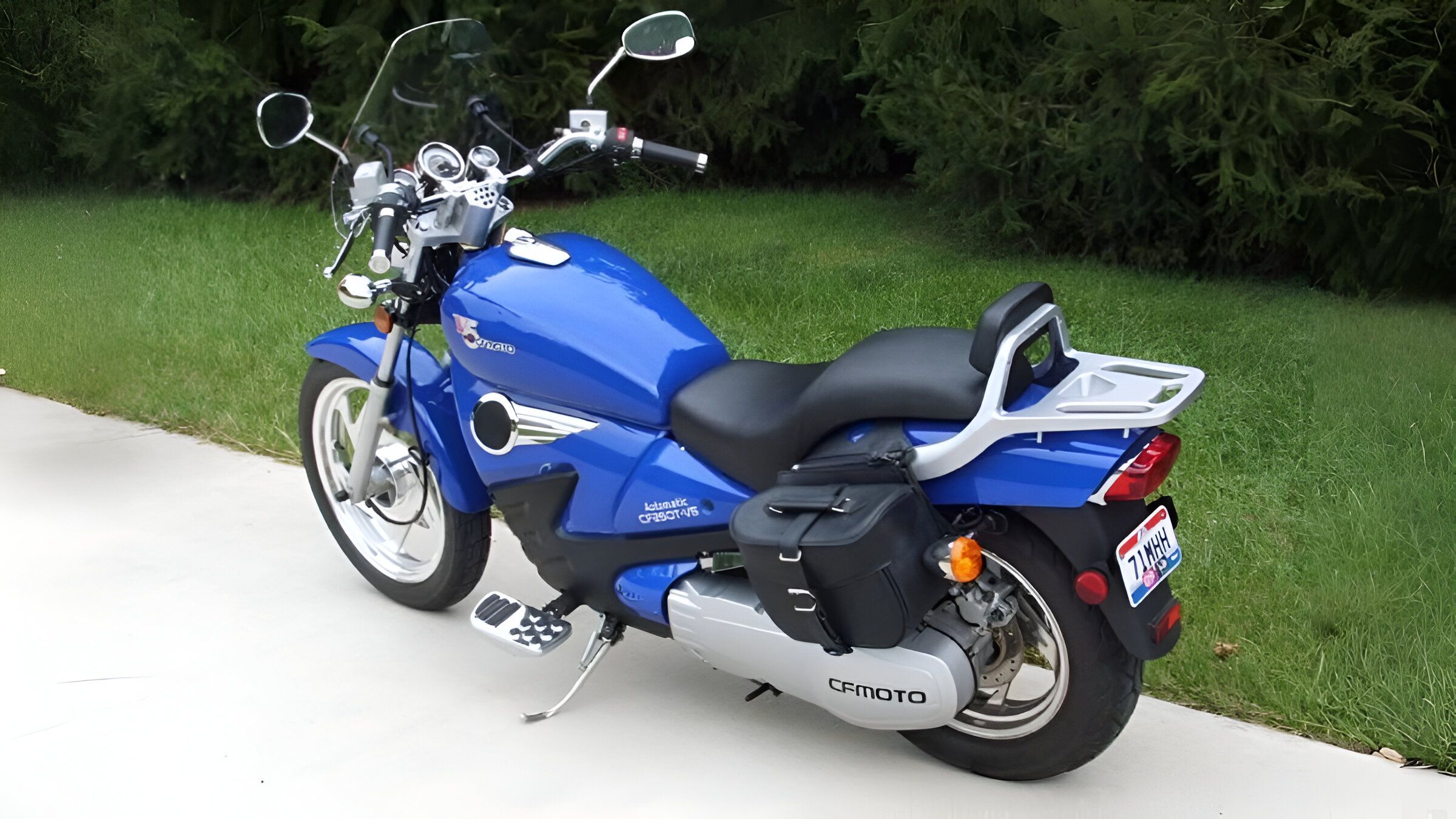
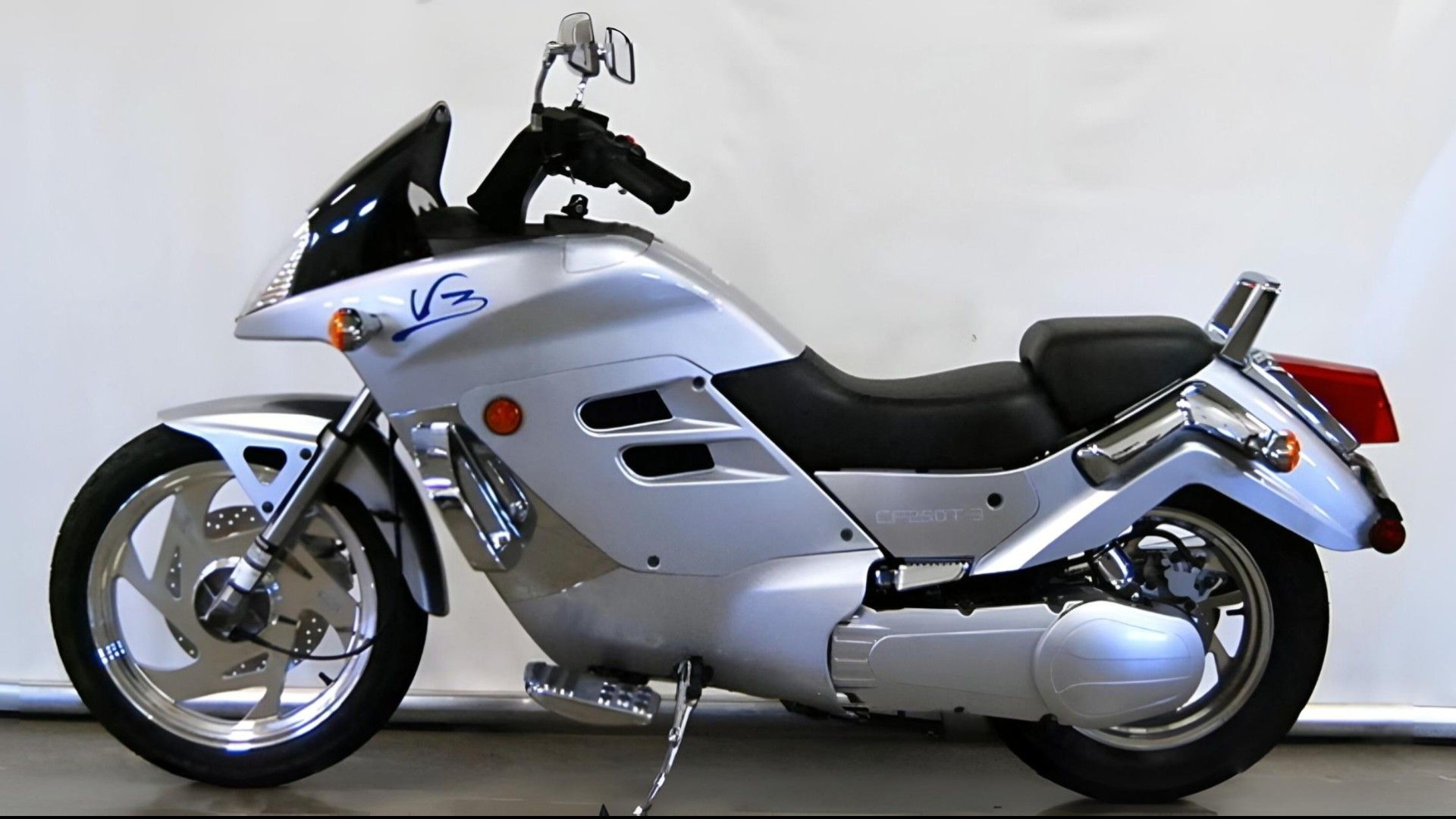
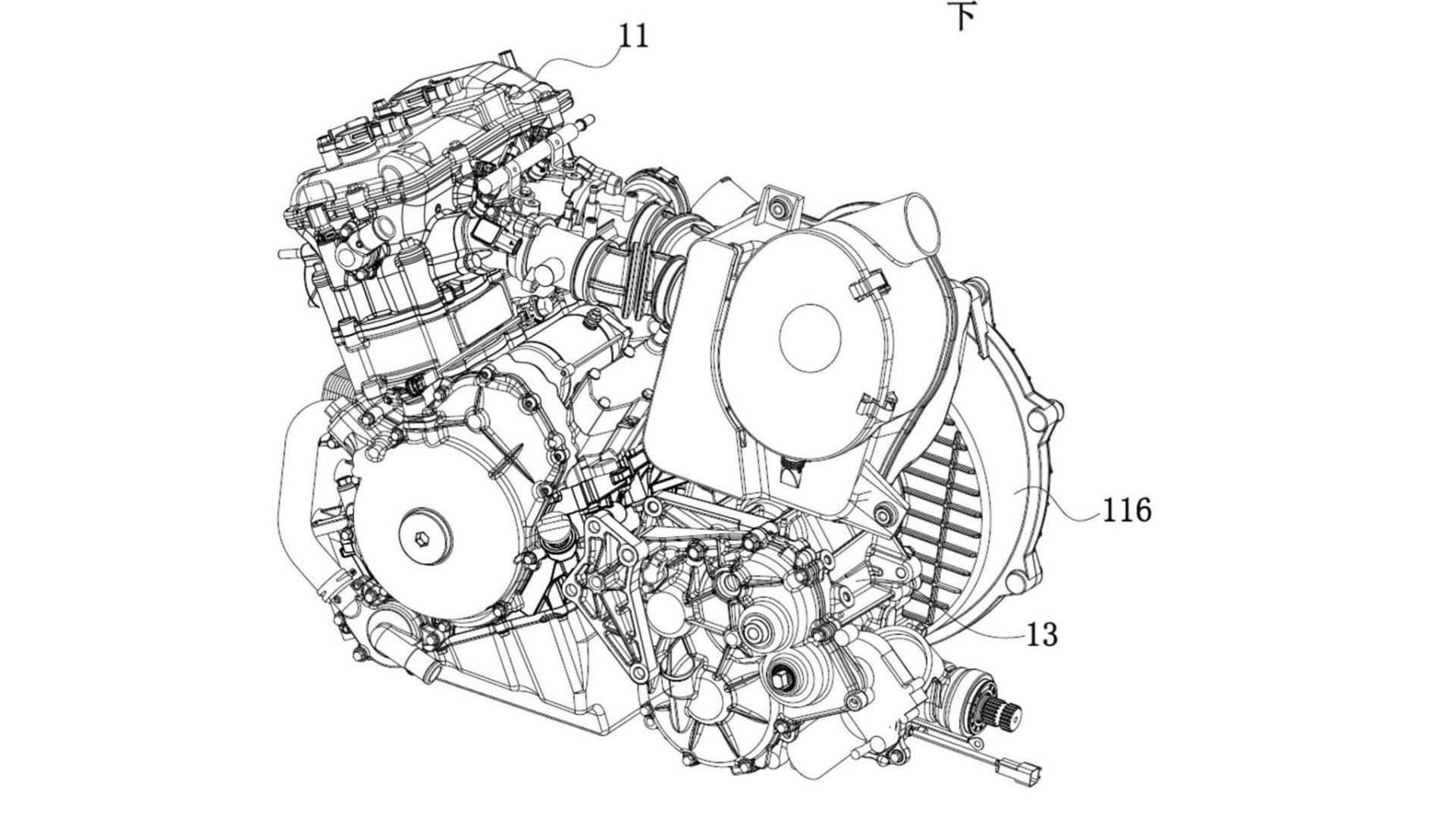
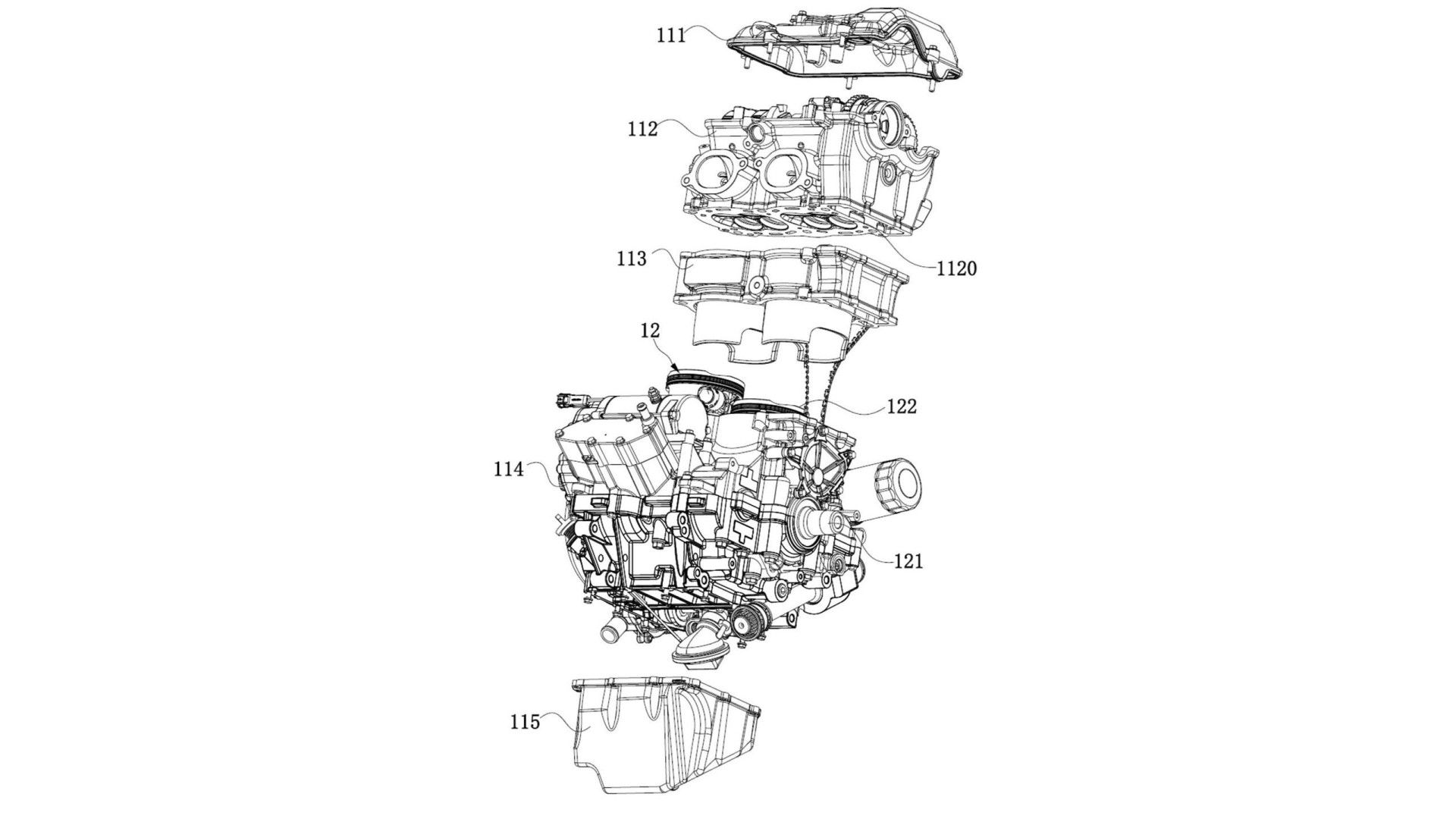
This is not the first time CFMoto is planning to install a CVT transmission on a motorcycle. The brand did it in the early 2000s with the radically designed V3 Sport and V5 cruiser bikes. But those were heavy bikes with a humble single-cylinder engine producing under 20 horsepower. These patents show a parallel-twin engine, the design of which doesn’t match any CFMoto current engine portfolio. So, it is going to be an all-new powertrain. The images show us elements like chain-driven double-overhead cams and a component that looks like a cam phaser fixed to the intake camshaft sprocket.
How Does A CVT Gearbox Work?
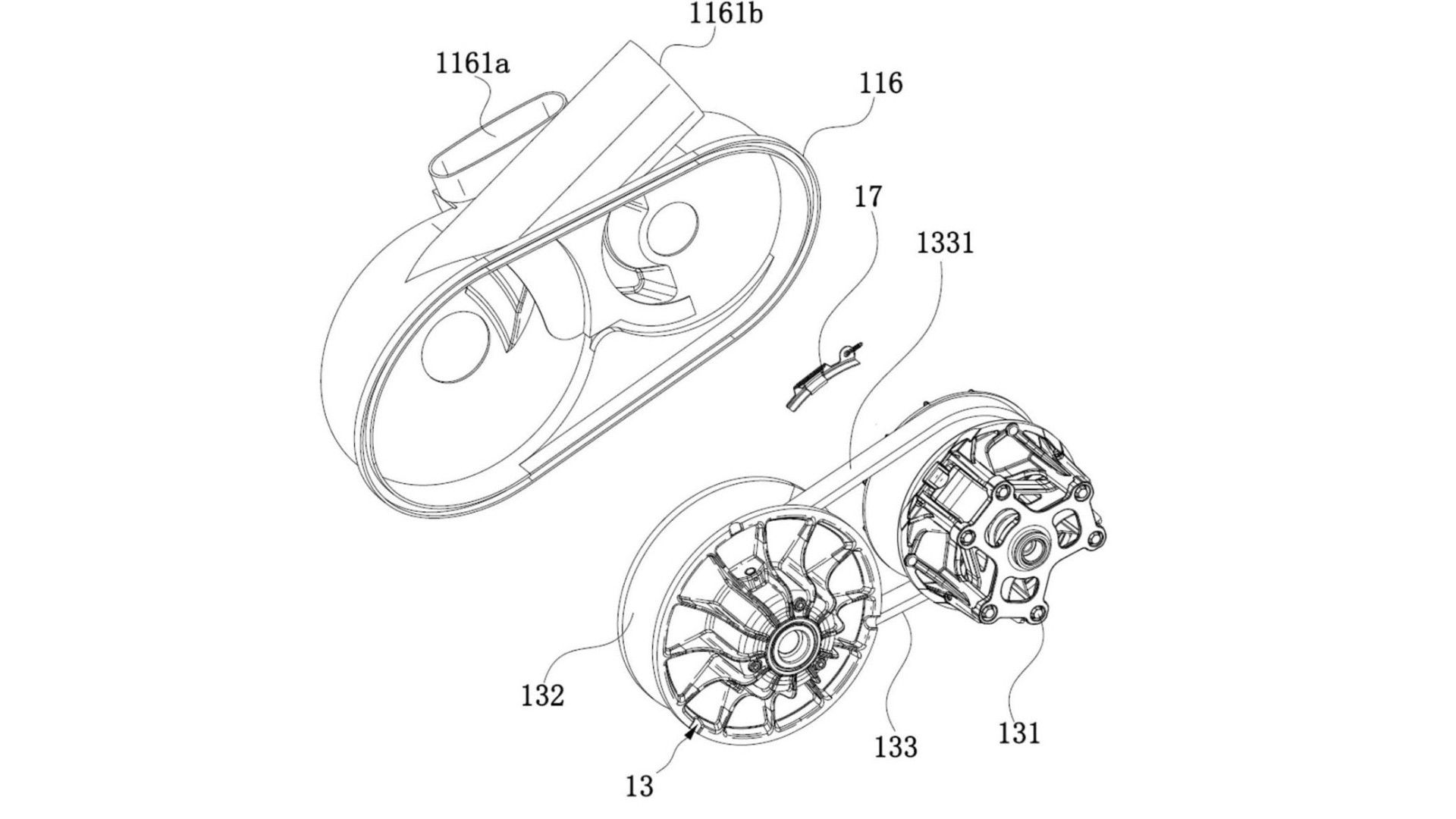
The major components in a CVT gearbox include two pulleys with a belt wrapped between them. One of the pulleys is attached to the engine via a centrifugal clutch and the other to the wheel via a bevel-gear-driven shaft drive. Both pulleys have movable cone-shaped halves that slide inwards or outward under centrifugal force. This allows a CVT transmission to have an infinite number of gear ratios. The rear pulley has a set of dynamic rollers on the movable part.
Under acceleration, these rollers move outwards due to centrifugal force, which in turn makes the cone-shaped component slide inwards. This increases the diameter of the contact patch and stiffens the belt. At the same time, the movable section of the pulley on the engine side expands. At maximum RPM, the belt drive has a ratio similar to the sixth gear on a motorcycle.